Kidney Transplant in India: Here’s Everything You Need to Know

Kidney Transplant
A kidney transplant is the transplant of a healthy donor’s kidney into the recipient with final-stage Renal disease. There are two types of Kidney transplantation in India, characteristically categorised as deceased-donor (cadaveric) or existing-donor transplant, which is purely reliant on the source of the donor organ. Existing donor renal transplantations are broadly categorized as hereditarily related or non-related transplants, conditional on whether a genetic association exists between the two.
The choice to undergo a kidney transplant is imperative. However, a kidney transplant is not a cure for renal disease. The decision to undergo this surgery demands life-long precautionary measure for the foreign kidney.
Why does a Kidney Transplant become Inevitable?
When a patient is diagnosed with renal failure, the kidneys fail to function and impede filtration of detrimental waste products; and hence, waste starts accumulating in the blood, thereby leading to a lethal condition called uremia.
However, when this happens, the patients are put on Dialysis- which helps in aiding the sieving of the wastes artificially but undergoing Dialysis is an arduous process and takes a toll on the patients.
Pre-emptive Procedure For kidney
A pre-emptive kidney transplant is a procedure which is performed before the kidney functioning worsens to the extent of performing dialysis to enhance the natural sieving function of the kidneys. Presently, most kidney transplants are performed on people who are undergoing dialysis because their kidneys fail to function efficiently.
Pre-emptive kidney procedure is the most preferred treatment for final-stage kidney disease, but U.S accounts for only about 20 percent of kidney transplants that are performed pre-emptively. Various factors have been associated with the lower than expected rate of pre-emptive kidney transplants-
- Dearth of Donor Kidneys
- Uneasy Access to Transplant Centres
- Dearth of Financial Aid for Socio-economic strata
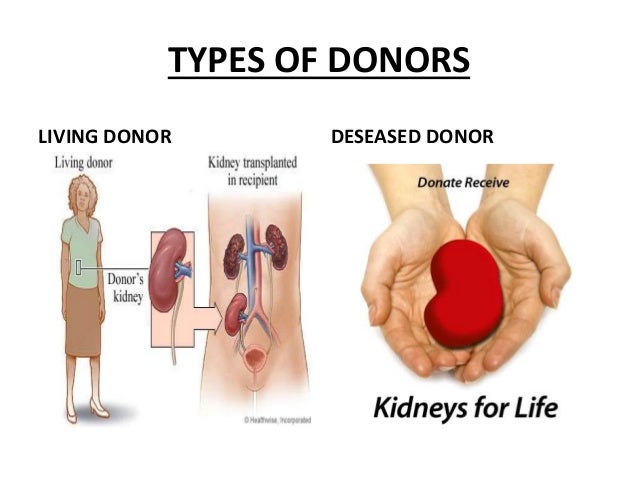
Types of Kidney Transplant
-
Deceased-donor kidney transplant
Also known as cadaver donor transplant, this procedure involves transplanting a healthy kidney from the deceased donor after seeking permission of the family and is placed in a recipient whose kidneys functionality has failed. The donor’s kidney is preserved in ice or is connected to the oxygen and nutrients until the organ is transplanted into the recipient. One donated kidney is sufficient to perform the renal functions efficiently. A living individual can donate a kidney, and living-donor kidney transplant is an alternative to a deceased-donor kidney transplant.
Deceased-donor kidney transplants in the US accounts for about two-thirds of the nearly 18,000 kidney transplants performed each year.
-
Living-donor kidney transplant
A living-donor kidney transplant involves removing a healthy kidney from a living donor and is surgically placed to a recipient whose kidneys fail to function. The living donor often is a biological family member (parent, sibling, or child). The living donor can also be a distant relative (uncle, aunt, friend, cousin, spouse or even a stranger). A kidney from a living donor usually gives immediate functioning post-transplant whereas a deceased donor kidney might take some days or maybe weeks to resume standard functionality.
The living donor transplant is scheduled as per the recipient and donor preparation time. As soon as the living donor kidney is available, the procedure must be performed. There are mitigated odds of rejection if the kidney donor is of the same blood group.
Techniques of Kidney Transplant Procedure
-
Traditional Open Nephrectomy
In Traditional Open Nephrectomy, larger incisions of about 6-8 inches length are made in your right after which the highly sterilised kidney is deployed into the recipient. When the procedure is completed, then the incisions are closed and cover with Steri-Strips. The entire process takes minimum three hours.
-
Laparoscopic Nephrectomy
Laparoscopic nephrectomy is performed in cases of a single artery to the left kidney unless this kidney is larger than the right one. The procedure involved usage of four trocars and the kidney are deployed through a 6 cm infra? umbilical incision.
Laparoscopic Nephrectomy holds potential in being minimally invasive to remove an infected kidney. When compared to traditional open surgery, laparoscopic nephrectomy holds potential in significantly less post-operative pain, a shorter hospital admittance, more promising cosmetic outcome when compared to the conventional procedure. The transplant is done under general anaesthesia, and the duration of the procedure is 3-4 hours.
-
Robotic Kidney Transplant
In a major novelty towards designing innovative techniques, nephrologists at Medanta Hospital, India and Henry Ford Hospital, Michigan have successfully transplanted kidneys into 50 recipients via a novel and ground-breaking robot-aided procedure. Highly being recognised as the ‘Icy’ technique, the procedure involves cooling the kidney with sterilized ice slush while the surgery is being performed.
The striking characteristic this surgery promises is a minimally invasive robotic procedure which mitigates post-surgery complications and helps alleviate post-operative pain. Close to 54 robot-assisted kidney transplants have been performed at Medanta Hospital and International Kidney and Renal Diseases, Ahmedabad has near about 56 successful Kidney Transplant to its credit.
The post-transplant scrutiny revealed a positive result, and it was observed that no patient complained of blood or urine leaks, contagions or any other complexity from their surgical wounds and the most promising aspect was that the likelihood of putting patients on dialysis post-surgery was eliminated. However, the approach warrants further research and investigations before robotic kidney transplant procedure is extensively adopted and practised in other hospitals both in India and globally.
Renal Transplant in India
It becomes inevitable for the caretakers of the patient and the patient himself to zero on other alternatives which are accessible at easy on the pocket cost in India, fret not; it’s an easy win in India. The primary encounters of therapeutic and surgical impediments of kidney transplantation have now been surpassed and presently, and the transplant centres proposing laparoscopic donor nephrectomy have been soaring in India.
With the advent of rapid technological explosion amidst the notion of artificial intelligence, some hospitals have also introduced robotic kidney transplantation in India. These novel techniques are being practised extensively, thereby opening boulevards to minimally invasive surgery. Also, the Indian hospitals are proficient in catering to all the services that meet the requirements of a global patient. From providing a world-class clean and friendly infrastructure to a range of healthy cuisines, they also lend their hands in delivering premium caregiving both before and post-transplant. Moreover, most of the doctors have collaborated with doctors worldwide. Hence it adds to the extra advantage of undergoing surgery in India.
Techniques Devoid of Post-Transplant Clinical Manifestations Sparks Hope
With the dawn of enhanced immunosuppressive pills and stimulation agents to put premature rejection occurrences at bay, Indian technologies have glimmered hope amongst the patients by switching from prescribing high-dose steroids to avert graft rejection, thereby mitigating the odds of complications post-transplant. Minimally invasive procedures for the effective management of transplant complications have been efficiently met due to the progress made in the field of nephrology and urology in the past few years.
Click here to know more about Documents Requirement for Renal Donor in India





